Док је петља позната и као претходно тестирана петља. Генерално, вхиле петља дозвољава да се део кода изврши више пута у зависности од датог логичког услова. Може се посматрати као изјава иф која се понавља. Док петља се углавном користи у случају када број итерација није унапред познат.
Синтакса вхиле петље у језику Ц
Синтакса вхиле петље у ц језику је дата у наставку:
while(condition){ //code to be executed } Дијаграм тока вхиле петље у Ц
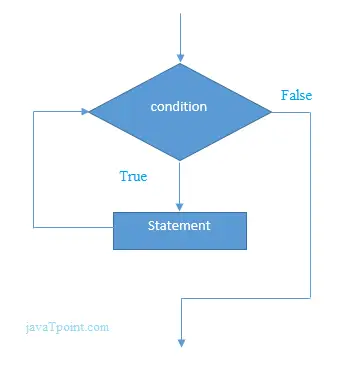
Пример вхиле петље у језику Ц
Хајде да видимо једноставан програм вхиле петље који штампа табелу 1.
#include int main(){ int i=1; while(i<=10){ printf('%d
',i); i++; } return 0; < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 </pre> <h2>Program to print table for the given number using while loop in C</h2> <pre> #include int main(){ int i=1,number=0,b=9; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); while(i<=10){ printf('%d
',(number*i)); i++; } return 0; < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> Enter a number: 50 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 </pre> <hr> <h2>Properties of while loop</h2> <ul> <li>A conditional expression is used to check the condition. The statements defined inside the while loop will repeatedly execute until the given condition fails.</li> <li>The condition will be true if it returns 0. The condition will be false if it returns any non-zero number.</li> <li>In while loop, the condition expression is compulsory.</li> <li>Running a while loop without a body is possible.</li> <li>We can have more than one conditional expression in while loop.</li> <li>If the loop body contains only one statement, then the braces are optional.</li> </ul> <h4>Example 1</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int j = 1; while(j+=2,j<=10) { printf('%d ',j); } printf('%d',j); < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> 3 5 7 9 11 </pre> <h4>Example 2</h4> <pre> #include void main () { while() { printf('hello Javatpoint'); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> compile time error: while loop can't be empty </pre> <h4>Example 3</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int x = 10, y = 2; while(x+y-1) { printf('%d %d',x--,y--); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h2>Infinitive while loop in C</h2> <p>If the expression passed in while loop results in any non-zero value then the loop will run the infinite number of times.</p> <pre> while(1){ //statement } </pre></=10)></pre></=10){></pre></=10){> Програм за штампање табеле за дати број користећи вхиле петљу у Ц
#include int main(){ int i=1,number=0,b=9; printf('Enter a number: '); scanf('%d',&number); while(i<=10){ printf(\'%d
\',(number*i)); i++; } return 0; < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> Enter a number: 50 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 </pre> <pre> Enter a number: 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 </pre> <hr> <h2>Properties of while loop</h2> <ul> <li>A conditional expression is used to check the condition. The statements defined inside the while loop will repeatedly execute until the given condition fails.</li> <li>The condition will be true if it returns 0. The condition will be false if it returns any non-zero number.</li> <li>In while loop, the condition expression is compulsory.</li> <li>Running a while loop without a body is possible.</li> <li>We can have more than one conditional expression in while loop.</li> <li>If the loop body contains only one statement, then the braces are optional.</li> </ul> <h4>Example 1</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int j = 1; while(j+=2,j<=10) { printf(\'%d \',j); } printf(\'%d\',j); < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> 3 5 7 9 11 </pre> <h4>Example 2</h4> <pre> #include void main () { while() { printf('hello Javatpoint'); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> compile time error: while loop can't be empty </pre> <h4>Example 3</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int x = 10, y = 2; while(x+y-1) { printf('%d %d',x--,y--); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h2>Infinitive while loop in C</h2> <p>If the expression passed in while loop results in any non-zero value then the loop will run the infinite number of times.</p> <pre> while(1){ //statement } </pre></=10)></pre></=10){> Enter a number: 100 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Својства вхиле петље
- За проверу услова користи се условни израз. Наредбе дефинисане унутар вхиле петље ће се више пута извршавати све док дати услов не успе.
- Услов ће бити тачан ако врати 0. Услов ће бити нетачан ако врати било који број различит од нуле.
- У вхиле петљи, израз услова је обавезан.
- Покретање вхиле петље без тела је могуће.
- Можемо имати више од једног условног израза у вхиле петљи.
- Ако тело петље садржи само једну изјаву, онда су заграде опционе.
Пример 1
#include void main () { int j = 1; while(j+=2,j<=10) { printf(\'%d \',j); } printf(\'%d\',j); < pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> 3 5 7 9 11 </pre> <h4>Example 2</h4> <pre> #include void main () { while() { printf('hello Javatpoint'); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> compile time error: while loop can't be empty </pre> <h4>Example 3</h4> <pre> #include void main () { int x = 10, y = 2; while(x+y-1) { printf('%d %d',x--,y--); } } </pre> <h4>Output</h4> <pre> infinite loop </pre> <h2>Infinitive while loop in C</h2> <p>If the expression passed in while loop results in any non-zero value then the loop will run the infinite number of times.</p> <pre> while(1){ //statement } </pre></=10)> Пример 2
#include void main () { while() { printf('hello Javatpoint'); } } Излаз
compile time error: while loop can't be empty
Пример 3
#include void main () { int x = 10, y = 2; while(x+y-1) { printf('%d %d',x--,y--); } } Излаз
infinite loop
Инфинитив вхиле петља у Ц
Ако израз који је прослеђен у петљи вхиле резултира било којом вредношћу која није нула, онда ће се петља покренути бесконачан број пута.
while(1){ //statement } 