Можемо креирати јава програм за сортирање елемената низа користећи сортирање селекцијом. У алгоритму сортирања селекцијом тражимо најнижи елемент и распоређујемо га на одговарајућу локацију. Тренутни елемент мењамо следећим најмањим бројем.
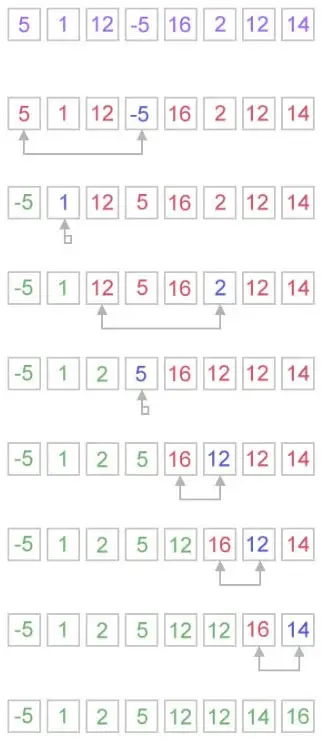
Како функционише селекција сортирања?
Алгоритам селекцијског сортирања ради на врло једноставан начин. Одржава два подниза за дати низ.
буцкет сорт
- Подниз је већ сортиран.
- А други подниз није сортиран.
Са сваком итерацијом сортирања селекцијом, елемент се бира из несортираног подниза и премешта у сортирани подниз.
јава итерација мапе
arr[] = 25 35 45 12 65 10 // Find the minimum element in arr[0...5] and place it at beginning. 10 25 35 45 12 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[1...5] and place it at beginning of arr[1...5] 10 12 25 35 45 65 // Find the minimum element in arr[2...5] and place it at beginning of arr[2...5] No, you can see that the array is already sorted. 10 12 25 35 45 65
Временска сложеност
Најбољи: ?(н^2)Просек: ?(н^2)
Најгоре: О(н^2)
Спаце Цомплекити
О(1)Избор сортирања Јава пример
public class SelectionSortExample { public static void selectionSort(int[] arr){ for (int i = 0; i <arr.length - 1; i++) { int index="i;" for (int j="i" + < arr.length; j++){ if (arr[j] arr[index]){ lowest } smallernumber="arr[index];" arr[index]="arr[i];" arr[i]="smallerNumber;" public static void main(string a[]){ int[] arr1="{9,14,3,2,43,11,58,22};" system.out.println('before selection sort'); for(int i:arr1){ system.out.print(i+' '); system.out.println(); selectionsort(arr1); sorting array using sort system.out.println('after pre> <p>Output:</p> <pre> Before Selection Sort 9 14 3 2 43 11 58 22 After Selection Sort 2 3 9 11 14 22 43 58 </pre> <h2>Selection Sort in Java (Another way)</h2> <p>You can also use a method where array is not predefined. Here, user has to put the elements as input.</p> <p>In the following Java program, we ask user to enter the array elements or number, now compare the array's element and start swapping with the variable temp. Put the first element in the temp and the second element in the first, and then temp in the second number and continue for the next match to sort the whole array in ascending order.</p> <pre> import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print('sorting array using selection sort technique..
'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print('now the after sorting is :
'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ ' '); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;></pre></arr.length> Сортирање избора у Јави (други начин)
Такође можете користити метод где низ није унапред дефинисан. Овде корисник мора да стави елементе као улаз.
У следећем Јава програму тражимо од корисника да унесе елементе низа или број, сада упореди елемент низа и почне да замењује са променљивом темп. Ставите први елемент у темп и други елемент у први, а затим темп у други број и наставите за следеће подударање да бисте сортирали цео низ у растућем редоследу.
import java.util.Scanner; public class SelectionSortExample2 { public static void main(String args[]) { int size, i, j, temp; int arr[] = new int[50]; Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print('Enter Array Size : '); size = scan.nextInt(); System.out.print('Enter Array Elements : '); for(i=0; i<size; i++) { arr[i]="scan.nextInt();" } system.out.print(\'sorting array using selection sort technique..
\'); for(i="0;" i<size; for(j="i+1;" j arr[j]) temp="arr[i];" arr[j]="temp;" system.out.print(\'now the after sorting is :
\'); system.out.print(arr[i]+ \' \'); < pre> <p>Output:</p> <strong> Use image SelectionSort</strong> </size;>