Доношење одлука је најважнији аспект скоро свих програмских језика. Као што назив имплицира, доношење одлука нам омогућава да покренемо одређени блок кода за одређену одлуку. Овде се доносе одлуке о валидности одређених услова. Провера стања је окосница доношења одлука.
азбука по броју
У Питхон-у, доношење одлука се врши помоћу следећих изјава.
| Изјава | Опис |
|---|---|
| Иф Статемент | Наредба иф се користи за тестирање одређеног стања. Ако је услов тачан, блок кода (иф-блок) ће бити извршен. |
| Иф - елсе Изјава | Наредба иф-елсе је слична иф наредби осим чињенице да такође обезбеђује блок кода за лажни случај услова који треба проверити. Ако је услов дат у наредби иф нетачан, онда ће се извршити наредба елсе. |
| Угнежђена изјава иф | Угнежђени иф изрази нам омогућавају да користимо иф ? елсе наредба унутар спољне иф наредбе. |
Увлачење у Питхон-у
Ради лакшег програмирања и постизања једноставности, питхон не дозвољава употребу заграда за код на нивоу блока. У Питхон-у се увлачење користи за декларисање блока. Ако су два исказа на истом нивоу увлачења, онда су они део истог блока.
Генерално, четири размака се дају за увлачење изјава које су типична количина увлачења у Питхон-у.
Увлачење је део језика Питхон који се најчешће користи јер декларише блок кода. Сви искази једног блока су намењени увлачењу истог нивоа. Видећемо како се стварно увлачење одвија у доношењу одлука и другим стварима у Питхон-у.
Изјава иф
Наредба иф се користи за тестирање одређеног услова и ако је услов тачан, извршава блок кода познат као иф-блок. Услов иф исказа може бити било који важећи логички израз који се може проценити на тачно или нетачно.
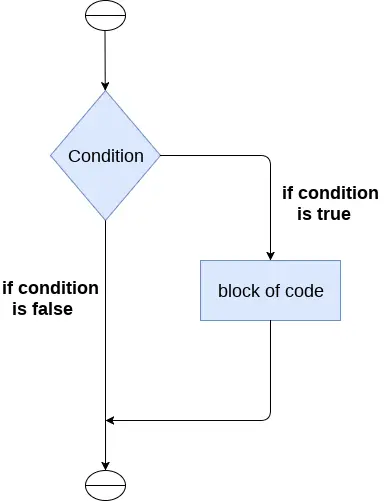
Синтакса иф-наредбе је дата у наставку.
if expression: statement
Пример 1
# Simple Python program to understand the if statement num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number')
Излаз:
enter the number: 10 The Given number is an even number
Пример 2: Програм за штампање највећег од три броја.
# Simple Python Program to print the largest of the three numbers. a = int (input('Enter a: ')); b = int (input('Enter b: ')); c = int (input('Enter c: ')); if a>b and a>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given a is largest'); if b>a and b>c: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given b is largest'); if c>a and c>b: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print ('From the above three numbers given c is largest');
Излаз:
није једнако мискл
Enter a: 100 Enter b: 120 Enter c: 130 From the above three numbers given c is largest
Изјава иф-елсе
Наредба иф-елсе обезбеђује блок елсе у комбинацији са иф наредбом која се извршава у лажном случају услова.
Ако је услов тачан, онда се иф-блок извршава. У супротном, елсе-блок се извршава.

Синтакса иф-елсе изјаве је дата у наставку.
if condition: #block of statements else: #another block of statements (else-block)
Пример 1: Програм за проверу да ли особа има право гласа или не.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a person is eligible to vote or not. age = int (input('Enter your age: ')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if age>=18: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('You are eligible to vote !!'); else: print('Sorry! you have to wait !!');
Излаз:
Enter your age: 90 You are eligible to vote !!
Пример 2: Програм за проверу да ли је број паран или не.
# Simple Python Program to check whether a number is even or not. num = int(input('enter the number:')) # Here, we are taking an integer num and taking input dynamically if num%2 == 0: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The Given number is an even number') else: print('The Given Number is an odd number')
Излаз:
листинг јава
enter the number: 10 The Given number is even number
Изјава елиф
Наредба елиф нам омогућава да проверимо више услова и извршимо одређени блок наредби у зависности од истинитог услова међу њима. Можемо имати било који број елиф изјава у нашем програму у зависности од наших потреба. Међутим, коришћење елифа је опционо.
Наредба елиф функционише као иф-елсе-иф мердевина изјава у Ц. Мора бити наследјена иф наредбом.
Синтакса елиф исказа је дата у наставку.
if expression 1: # block of statements elif expression 2: # block of statements elif expression 3: # block of statements else: # block of statements

Пример 1
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement number = int(input('Enter the number?')) # Here, we are taking an integer number and taking input dynamically if number==10: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equals to 10') elif number==50: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 50'); elif number==100: # Here, we are checking the condition. If the condition is true, we will enter the block print('The given number is equal to 100'); else: print('The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100');
Излаз:
Enter the number?15 The given number is not equal to 10, 50 or 100
Пример 2
# Simple Python program to understand elif statement marks = int(input('Enter the marks? ')) # Here, we are taking an integer marks and taking input dynamically if marks > 85 and marks 60 and marks 40 and marks 30 and marks <= 40): # here, we are checking the condition. if condition is true, will enter block print('you scored grade c ...') else: print('sorry you fail ?') < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter the marks? 89 Congrats ! you scored grade A ... </pre> <hr></=> 