Висина или дубина бинарног стабла се може дефинисати као максимални или највећи број ивица од лисног чвора до коренског чвора или коренског чвора до лисног чвора. Коријенски чвор ће бити на нултом нивоу, што значи да ако коријенски чвор нема ниједан подређени чвор повезан са њим, онда се каже да је висина или дубина одређеног бинарног стабла нула.
Узмимо пример за боље разумевање висине бинарног стабла.
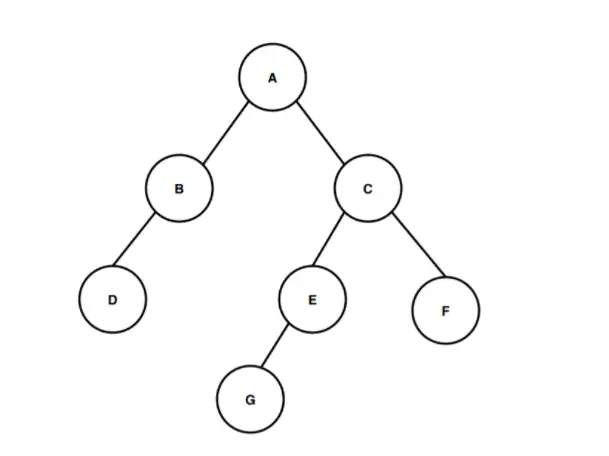
На горњој слици имамо бинарно стабло које почиње од коренског чвора по имену А. Коренски чвор А има два подређена чвора Б и Ц као лево дете и десно дете. И слично, леви подређени чвор Б има само један леви подређени чвор по имену Д, а десни подређени чвор Ц има два подређена чвора Е и Ф од којих чвор Е има чвор Г као једино лево дете.
датум претворити у стринг
Хајде сада да израчунамо висину овог бинарног стабла. Избројите број ивица почевши од коренског чвора до најдубљег лисног чвора за израчунавање висине бинарног стабла. Најдубљи чвор који је присутан у овом бинарном стаблу је чвор Г. Дакле, за израчунавање висине или дубине овог бинарног стабла треба да израчунамо број ивица између коренског чвора и најдубљег чвора Г. Прва ивица је од чвора А до чвора Ц, друга ивица је од чвора Ц до чвора Е и трећа ивица је од чвора Е до чвора Г. Дакле, за прелазак од коренског чвора А до најдубљег чвора Г постоје три ивице , па је висина или дубина бинарног стабла 3. Пут којим смо се кретали од корена до најдубљег лисног чвора је А > Ц > Е > Г и ова путања покрива три ивице током обиласка, зато према према дефиницији висине бинарног стабла висина овог бинарног стабла је 3.
Начини за проналажење висине бинарног стабла
Сада, хајде да напишемо код да пронађемо висину бинарног стабла. Постоје два начина да пронађете висину бинарног стабла. Један је рекурзивни метод а други је нерекурзивни метод који ће користити структуру података Куеуе за израчунавање висине бинарног стабла.
Рекурзивни начин
Прво, да видимо рекурзивни начин за проналажење висине бинарног стабла.
код:
// Java program to create and to find the height of a binary tree by recursive way // util package is imported to use classes like Queue and LinkedList import java.util.*; // A class named Node is created representing a single node of a binary tree class Node{ // The class Node has three class variables named key and left and right of int type and Node type respectively. // the key variable holds the actual value that is assigned to that node of the binary tree int key; // left and right variables that are of Node type will be used to store the left and right child nodes of the parent of the binary tree Node left, right; // a parameterized constructor is created to create and add data to the node at the same time. public Node(int item) { key = item; left = right = null; } } // end of node class definition // A public class named BinaryTree is created having two constructors and methods to print the binary tree level-wise. class BinaryTree{ // A static variable named root_node is created that will represent the node of the binary tree static Node root_node; // A parametrized constructor of the BinaryTree class is written having the key as a parameter BinaryTree(int key) { // here we are constructing a new node and assigning it to the root node root_node = new Node(key); } BinaryTree() { root_node = null; } // a public static function named print tree is created to print all the nodes in the tree level-wise starting from the root node public static void printTree() { int h = height(root_node); int i; for (i=1; i<=h; i++){ printcurrentlevel(root_node, i); system.out.println(); } a public static function named height is created to fund the of binary tree starting from root node deepest leaf that present in passed as parameter called recursively until returned null find int height(node root){ then will be zero if (root="=" null) return 0; else { * compute each subtree lheight="height(root.left);" rheight="height(root.right);" use larger one both sub trees calcualted and which higher used. (lheight> rheight) return(lheight+1); else return(rheight+1); } } // a Public static function named printCurrentLevel is created to print al the nodes that are present in that level // this function is called repeatedly for each level of the binary tree to print all the nodes in that particular level public static void printCurrentLevel (Node root ,int level) { if (root == null) return; if (level == 1) System.out.print(root.key + ' '); else if (level > 1) { printCurrentLevel(root.left, level-1); printCurrentLevel(root.right, level-1); } } //the main function is created to create an object of the BinaryTree class and call the printTree method to level-wise print the nodes of the binary tree and the height method to find the height of the binary tree public static void main(String[] args){ // first of all we have created an Object of the BinaryTree class that will represent the binary tree BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree(); // now a new node with the value as 150 is added as the root node to the Binary Tree tree.root_node = new Node(150); // now a new node with the value 250 is added as a left child to the root node tree.root_node.left = new Node(250); // now a new node with the value 270 is added as a right child to the root node tree.root_node.right = new Node(270); // now a new node with the value 320 is added as a left child to the left node of the previous level node tree.root_node.left.left = new Node(320); // now a new node with the value 350 is added as a right child to the right node of the previous level node tree.root_node.left.right = new Node(350); /* 150 / 250 270 / / 320 350 null null */ System.out.println('Printing the nodes of tree level wise :'); System.out.println('Level order traversal : '); tree.printTree(); // height of the binary tree is calculated bypassing the root as parameter to the height() function. int h = tree.height(tree.root_node) System.out.println('The height of the Binary tree is : ' + h ); } } // end of the BinaryTree class </=h;> Излаз: Излаз горњег кода је:
Printing the nodes of tree level wise: Level order traversal: (level 0) 150 (level 1) 250 270 (level 2) 320 350 The height of the Binary tree is: 2
На рекурзиван начин, позвали смо висина () функција више пута да пронађе висину бинарног стабла. Основни чвор бинарног стабла се прослеђује као параметар функцији хеигхт(). Висина() функција израчунава висину оба подстабла коренског чвора и која од обе висине је већа сматра се висином бинарног стабла.
Нерекурзивни начин
Погледајмо сада нерекурзивни начин за проналажење висине бинарног стабла.
код:
стринг у логички јава
// A C++ program to create and to find the height of a binary tree by non recursive way // iostream header file is included to use the cin and cout objects of the istream and ostream classes respectively #include #include using namespace std; // A struct named Node is created representing a single node of a binary tree struct Node { // The struct Node has three variables named key and left and right of int type and Node type respectively. // the key variable holds the actual value that is assigned to that node of the binary tree int key; // left and right variables that are of Node type will be used to store the left and right child nodes of the parent of the binary tree struct Node* left, *right; }; // A Function named newNode is created to add a new node to the binary tree, the newNode function has one parameter of integer type named key that will represent the value that particular new node will be storing Node* newNode(int key) { Node* temp = new Node; temp->key = key; temp->left = temp->right = NULL; return (temp); } // A function named height is created to find the height of the binary tree with non recursive way // The parameter to the height function is the root node of the binary tree that will be present at level zero // In the height function the nodes of the binary tree are added into the Queue data structure and the depth variable is incremented until // the NULL node is encountered while traversing the nodes of the binary tree stored in the Queue data structure. int height(struct Node* root){ //Initialising a variable to count the //height of tree int depth = 0; queueq; //Pushing first level element along with NULL q.push(root); q.push(NULL); while(!q.empty()){ Node* temp = q.front(); q.pop(); //When NULL encountered, increment the value if(temp == NULL){ depth++; } //If NULL not encountered, keep moving if(temp != NULL){ if(temp->left){ q.push(temp->left); } if(temp->right){ q.push(temp->right); } } //If queue still have elements left, //push NULL again to the queue. else if(!q.empty()){ q.push(NULL); } } return depth; } // Start of the main function int main() { // first of all we have created an Object of the struct Node that will represent the binary tree // the value of the root node is 10 Node *root = newNode(10); // now a new node with the value 20 is added as a left child to the root node root->left = newNode(20); // now a new node with the value 30 is added as a right child to the root node root->right = newNode(30); // now a new node with the value 40 is added as a left child to the left node of the previous level node root->left->left = newNode(40); // now a new node with the value 50 is added as a right child to the left node of the previous level node root->left->right = newNode(50); /* 10 / 20 30 / / 40 50 null null */ cout<<'the height(depth) of tree is: '<<height(root); cout<<endl; } end the main function < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> The Height(Depth) of the tree is: 2 </pre> <p>In this approach, we have used a non recursive way to find the depth of the binary tree. To find the height of the binary tree, we have written a function named height that will require a parameter of Node type (that means the root of the binary tree whose height needs to be calculated). The root of the binary tree is present at level zero, which means the height or depth of the root is zero.</p> <p>In the non recursive approach, we use the Queue Data Structure to find the depth of the binary tree. The nodes of the binary tree for which we want to find the depth are added to the Queue data structure with the help of an enqueue operation to which the node of the binary tree is passed as a parameter to this function.</p> <p>Once all the nodes are added to the queue, the nodes added in the queue are removed by calling the dequeue function that will keep on removing one element from the queue until the null node of the binary tree is encountered. Each time a node of the binary tree from the queue is removed, the depth variable representing the depth of the binary tree is incremented by one. And in the end, the value of the depth variable will represent the final depth of the binary tree.</p> <hr></'the> У овом приступу, користили смо нерекурзивни начин да пронађемо дубину бинарног стабла. Да бисмо пронашли висину бинарног стабла, написали смо функцију под називом висина која ће захтевати параметар типа Ноде (то значи корен бинарног стабла чију висину треба израчунати). Корен бинарног стабла је присутан на нултом нивоу, што значи да је висина или дубина корена нула.
У нерекурзивном приступу, користимо структуру података реда да пронађемо дубину бинарног стабла. Чворови бинарног стабла за које желимо да пронађемо дубину додају се структури података Куеуе уз помоћ енкуеуе операције којој се чвор бинарног стабла прослеђује као параметар овој функцији.
Када се сви чворови додају у ред, чворови додати у ред се уклањају позивањем функције декуеуа која ће наставити да уклања један елемент из реда све док се не наиђе на нулти чвор бинарног стабла. Сваки пут када се чвор бинарног стабла уклони из реда, променљива дубине која представља дубину бинарног стабла се повећава за један. И на крају, вредност променљиве дубине представљаће коначну дубину бинарног стабла.
