Низ је најједноставнија структура података у Ц која складишти хомогене податке на суседним меморијским локацијама. Ако желимо да креирамо низ, декларишемо тип података и дајемо елементе у њега:
#include int main() { int i, arr[5] = {1, 2, 4, 2, 4}; for(i = 0; i <5; i++) { printf('%d ', arr[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> 1 2 4 2 4 </pre> <p>In C, a Character and a String are separate data types, unlike other programming languages like Python. A String is a collection of Characters. Hence, to define a String, we use a Character Array:</p> <pre> #include int main() { char str[8]; printf('Enter a String: '); scanf('%s', &str); printf('%s', str); } </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> Enter a String: Hello Hello </pre> <p>Now, we want to create an Array of Strings which means we are trying to create an Array of Character Arrays. We have two ways we can do this:</p> <ol class="points"> <li>Using Two-dimensional Arrays</li> <li>Using Pointers</li> </ol> <h3>Using Two-dimensional Arrays:</h3> <p>Creating a String Array is one of the applications of two-dimensional Arrays. To get a picture of the arrangement, observe the below representation:</p> <p>For suppose we want to create an Array of 3 Strings of size 5:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p>Every String in a String Array must terminate with a null Character. It is the property of a String in C.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create a 2D Array:</strong> </p> <pre> Data_type name[rows][columns] = {{values in row 1}, {values in row 2}…}; </pre> <p> <strong>Syntax to create a String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> char Array[rows][columns] = {'String1', 'String2'...}; </pre> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <ul> <li>Observe that when we assign the number of rows and columns, we need to consider the Null Character to the length.</li> </ul> <pre> #include int main() { int i; char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Black Blame Block </pre> <ul> <li>char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Black'} -> {{'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'm', 'e', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}}</li> <li>We cannot directly manipulate the Strings in the Array as a String is an immutable data type. The compiler raises an error:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[0] = 'Hello'; </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> [Error] assignment to expression with Array type </pre> <ul> <li>We can use the strcpy() function to copy the value by importing the String header file:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf('%s
', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;></pre></3;></pre></5;> У Ц-у, карактер и стринг су одвојени типови података, за разлику од других програмских језика као што је Питхон. Стринг је колекција знакова. Дакле, да дефинишемо стринг, користимо низ знакова:
#include int main() { char str[8]; printf('Enter a String: '); scanf('%s', &str); printf('%s', str); } Излаз:
Enter a String: Hello Hello
Сада желимо да креирамо низ низова што значи да покушавамо да креирамо низ низова знакова. Имамо два начина да то урадимо:
- Коришћење дводимензионалних низова
- Коришћење показивача
Коришћење дводимензионалних низова:
Креирање низа низова је једна од примена дводимензионалних низова. Да бисте добили слику аранжмана, погледајте доњи приказ:
Претпоставимо да желимо да креирамо низ од 3 низа величине 5:
јава дуг за низ
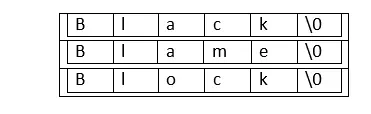
Сваки стринг у низу стрингова мора се завршити нултим знаком. То је својство стринга у Ц.
Синтакса за креирање 2Д низа:
Data_type name[rows][columns] = {{values in row 1}, {values in row 2}…}; Синтакса за креирање низа низова:
char Array[rows][columns] = {'String1', 'String2'...}; Сада, хајде да направимо пример низа низова:
- Запазите да када додељујемо број редова и колона, морамо узети у обзир нулти карактер дужини.
#include int main() { int i; char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Black Blame Block </pre> <ul> <li>char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Black'} -> {{'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'm', 'e', '�'}, {'B', 'l', 'a', 'c', 'k', '�'}}</li> <li>We cannot directly manipulate the Strings in the Array as a String is an immutable data type. The compiler raises an error:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[0] = 'Hello'; </pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> [Error] assignment to expression with Array type </pre> <ul> <li>We can use the strcpy() function to copy the value by importing the String header file:</li> </ul> <pre> char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;></pre></3;> - цхар Арраи[3][6] = {'Црно', 'Окривљавање', 'Црно'} -> {{'Б', 'л', 'а', 'ц', 'к', '�' }, {'Б', 'л', 'а', 'м', 'е', '�'}, {'Б', 'л', 'а', 'ц', 'к', '�'}}
- Не можемо директно да манипулишемо стринговима у низу јер је стринг непроменљив тип података. Компајлер јавља грешку:
char Array[0] = 'Hello';
Излаз:
[Error] assignment to expression with Array type
- Можемо да користимо функцију стрцпи() да копирамо вредност увозом датотеке заглавља стринга:
char Array[3][6] = {'Black', 'Blame', 'Block'}; strcpy(Array[0], 'Hello'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: Hello Blame Block </pre> <p> <strong>The Disadvantage of using 2D Arrays:</strong> </p> <p>Suppose we want to store 4 Strings in an Array: {'Java', 'T', 'point', 'JavaTpoint'}. We will store the Strings like this:</p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-2.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <ul> <li>The number of rows will be equal to the number of Strings, but the number of columns will equal the length of the longest String.</li> <li>The memory allocated to all the Strings will be the size of the longest String, causing ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> '.</li> <li>The orange part in the above representation is the memory wasted.</li> </ul> <h3>Using Pointers:</h3> <p>By using Pointers, we can avoid the Disadvantage of Memory wastage. But how do we do this?</p> <p>We need to create an Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Hence, we need to create an Array of type ' <strong>char*</strong> '. This way, all the Strings are stored elsewhere in the exactly needed memory, and the Pointers in the Array point to those memory locations causing no memory wastage. More specifically, the Pointers in the Array point to the first Character of the Strings.</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Data Type* name[] = {'Value 1', 'Value 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Syntax to create an Array of String Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>char* Array[] = {'String 1', 'String 2'…};</p> <p> <strong>Representation:</strong> </p> <img src="//techcodeview.com/img/c-tutorial/46/an-array-strings-c-3.webp" alt="An Array of Strings in C"> <p> <strong>Now, let us create an example String Array:</strong> </p> <pre> #include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;></pre></3;> Недостаци коришћења 2Д низова:
Претпоставимо да желимо да ускладиштимо 4 стринга у низу: {'Јава', 'Т', 'поинт', 'ЈаваТпоинт'}. Стрингове ћемо чувати овако:

- Број редова ће бити једнак броју стрингова, али ће број колона бити једнак дужини најдужег низа.
- Меморија додељена свим стринговима биће величине најдужег стринга, узрокујући ' Расипање меморије '.
- Наранџасти део у горњој представи је изгубљена меморија.
Коришћење показивача:
Коришћењем показивача, можемо избећи недостатак меморије. Али како да ово урадимо?
јава за типове петљи
Морамо да направимо низ показивача који показују на стрингове. Дакле, морамо да креирамо низ типа ' цхар* '. На овај начин, сви стрингови се чувају негде другде у тачно потребној меморији, а показивачи у низу указују на те меморијске локације које не изазивају губитак меморије. Тачније, показивачи у низу указују на први карактер стрингова.
Синтакса за креирање низа показивача:
Тип података* наме[] = {'Вредност 1', 'Вредност 2'…};
кор у јава
Синтакса за креирање низа стринг поинтера:
цхар* Арраи[] = {'Стринг 1', 'Стринг 2'…};
Репрезентација:

Сада, хајде да направимо пример низа низова:
#include #include int main() { int i; char* Array[] = {'HI', 'UP', 'AT'}; printf('String Array:
'); for(i = 0; i <3; i++) { printf(\'%s
\', array[i]); } return 0; < pre> <p> <strong>Output:</strong> </p> <pre> String Array: HI UP AT </pre> <h3>Summary:</h3> <p>We cannot create a String Array like a normal one, as a String is an Array of Characters. We have two ways to do this:</p> <p> <strong>1. Using a Two-Dimensional Array:</strong> </p> <p>The Disadvantage of using this way is ' <strong>Memory wastage</strong> ,' as the memory allocated to every String in the Array will be the memory required to store the longest String of the Array.</p> <p> <strong>2. Using Pointers:</strong> </p> <p>Using Pointers, we create a single-dimensional Array of Pointers pointing to Strings. Following this method can eliminate the 'Memory wastage' Disadvantage.</p> <hr></3;> резиме:
Не можемо креирати низ знакова као нормалан, јер је стринг низ знакова. Имамо два начина да то урадимо:
1. Коришћење дводимензионалног низа:
Недостатак коришћења овог начина је ' Расипање меморије ,' пошто ће меморија додељена сваком стрингу у низу бити меморија потребна за чување најдужег стринга низа.
2. Коришћење показивача:
Користећи показиваче, креирамо једнодимензионални низ показивача који показују на низове. Праћење овог метода може да елиминише недостатак „трошења меморије“.
