 #працтицеЛинкДив { дисплаи: ноне !импортант; }
#працтицеЛинкДив { дисплаи: ноне !импортант; }Алгоритам обрнутог брисања је уско повезан са Крускалов алгоритам . У Крускаловом алгоритму оно што радимо је: сортирање ивица по растућем редоследу њихових тежина. Након сортирања, једну по једну бирамо ивице у растућем редоследу. Укључујемо тренутну изабрану ивицу ако укључивањем ове у разапињуће стабло не формира никакав циклус све док не постоје В-1 ивице у разапињућем стаблу где је В = број врхова.
У алгоритму обрнутог брисања сортирамо све ивице опадајући редослед њихових тежина. Након сортирања, једну по једну бирамо ивице у опадајућем редоследу. Ми укључи тренутну изабрану ивицу ако изузимање тренутне ивице узрокује прекид везе у струјном графикону . Главна идеја је брисање ивице ако њено брисање не доводи до прекида везе графа.
систем.оут.принтлн
Алгоритам:
- Сортирај све ивице графа по нерастућем редоследу тежина ивица.
- Иницијализујте МСТ као оригинални граф и уклоните додатне ивице користећи корак 3.
- Изаберите ивицу највеће тежине са преосталих ивица и проверите да ли брисање ивице прекида везу са графиком или не .
Ако се прекине, не бришемо ивицу.
Иначе бришемо ивицу и настављамо.
Илустрација:
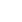
Хајде да разумемо следећи пример:
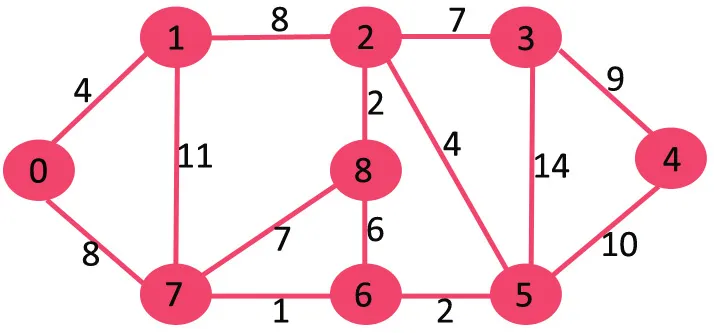
Ако избришемо највишу ивицу тежине 14, граф се не искључује па га уклањамо.
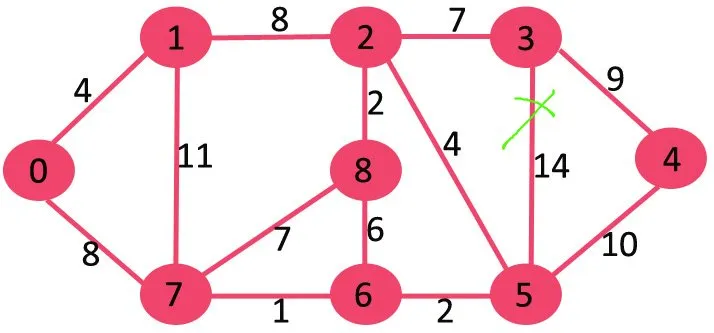
Затим бришемо 11 јер његово брисање не прекида везу са графиконом.
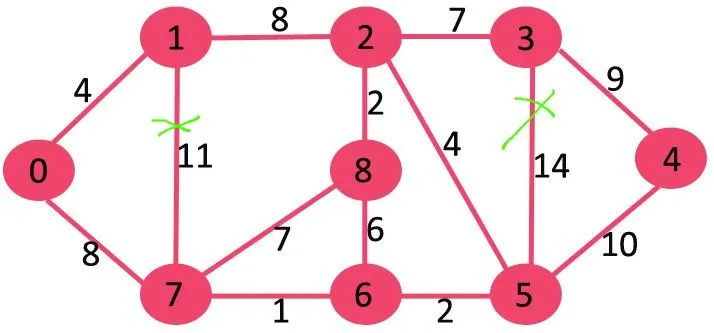
Затим бришемо 10 јер његово брисање не прекида везу са графиконом.

Следеће је 9. Не можемо да обришемо 9 јер његово брисање доводи до прекида везе.

Настављамо овим путем и следеће ивице остају у коначном МСТ.
Edges in MST
(3 4)
(0 7)
(2 3)
(2 5)
(0 1)
(5 6)
(2 8)
(6 7)
Напомена : У случају ивица исте тежине можемо одабрати било коју ивицу исте тежине ивица.
Препоручена пракса Алгоритам обрнутог брисања за минимално разапињуће стабло Покушајте!Имплементација:
C++// C++ program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm #include
// Java program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm import java.util.*; // class to represent an edge class Edge implements Comparable<Edge> { int u v w; Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.w = w; this.v = v; } public int compareTo(Edge other) { return (this.w - other.w); } } // Class to represent a graph using adjacency list // representation public class GFG { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<Integer>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; @SuppressWarnings({ 'unchecked' 'deprecated' }) public GFG(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new ArrayList[v]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>(); edges = new ArrayList<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v boolean[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex for (int i : adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private boolean IsConnected() { boolean[] visited = new boolean[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost Collections.sort(edges); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST System.out.println('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges.get(i).u; int v = edges.get(i).v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].remove(adj[u].indexOf(v)); adj[v].remove(adj[v].indexOf(u)); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].add(v); adj[v].add(u); // This edge is part of MST System.out.println('(' + u + ' ' + v + ')'); mst_wt += edges.get(i).w; } } System.out.println('Total weight of MST is ' + mst_wt); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; GFG g = new GFG(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by Prithi_Dey
# Python3 program to find Minimum Spanning Tree # of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm # Graph class represents a directed graph # using adjacency list representation class Graph: def __init__(self v): # No. of vertices self.v = v self.adj = [0] * v self.edges = [] for i in range(v): self.adj[i] = [] # function to add an edge to graph def addEdge(self u: int v: int w: int): self.adj[u].append(v) # Add w to v’s list. self.adj[v].append(u) # Add w to v’s list. self.edges.append((w (u v))) def dfs(self v: int visited: list): # Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = True # Recur for all the vertices adjacent to # this vertex for i in self.adj[v]: if not visited[i]: self.dfs(i visited) # Returns true if graph is connected # Returns true if given graph is connected else false def connected(self): visited = [False] * self.v # Find all reachable vertices from first vertex self.dfs(0 visited) # If set of reachable vertices includes all # return true. for i in range(1 self.v): if not visited[i]: return False return True # This function assumes that edge (u v) # exists in graph or not def reverseDeleteMST(self): # Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost self.edges.sort(key = lambda a: a[0]) mst_wt = 0 # Initialize weight of MST print('Edges in MST') # Iterate through all sorted edges in # decreasing order of weights for i in range(len(self.edges) - 1 -1 -1): u = self.edges[i][1][0] v = self.edges[i][1][1] # Remove edge from undirected graph self.adj[u].remove(v) self.adj[v].remove(u) # Adding the edge back if removing it # causes disconnection. In this case this # edge becomes part of MST. if self.connected() == False: self.adj[u].append(v) self.adj[v].append(u) # This edge is part of MST print('( %d %d )' % (u v)) mst_wt += self.edges[i][0] print('Total weight of MST is' mst_wt) # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': # create the graph given in above figure V = 9 g = Graph(V) # making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4) g.addEdge(0 7 8) g.addEdge(1 2 8) g.addEdge(1 7 11) g.addEdge(2 3 7) g.addEdge(2 8 2) g.addEdge(2 5 4) g.addEdge(3 4 9) g.addEdge(3 5 14) g.addEdge(4 5 10) g.addEdge(5 6 2) g.addEdge(6 7 1) g.addEdge(6 8 6) g.addEdge(7 8 7) g.reverseDeleteMST() # This code is contributed by # sanjeev2552
// C# program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm using System; using System.Collections.Generic; // class to represent an edge public class Edge : IComparable<Edge> { public int u v w; public Edge(int u int v int w) { this.u = u; this.v = v; this.w = w; } public int CompareTo(Edge other) { return this.w.CompareTo(other.w); } } // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation public class Graph { private int V; // No. of vertices private List<int>[] adj; private List<Edge> edges; public Graph(int v) // Constructor { V = v; adj = new List<int>[ v ]; for (int i = 0; i < v; i++) adj[i] = new List<int>(); edges = new List<Edge>(); } // function to Add an edge public void AddEdge(int u int v int w) { adj[u].Add(v); // Add w to v’s list. adj[v].Add(u); // Add w to v’s list. edges.Add(new Edge(u v w)); } // function to perform dfs private void DFS(int v bool[] visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; // Recur for all the vertices adjacent to // this vertex foreach(int i in adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) DFS(i visited); } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false private bool IsConnected() { bool[] visited = new bool[V]; // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (int i = 1; i < V; i++) { if (visited[i] == false) return false; } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not public void ReverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost edges.Sort(); int mst_wt = 0; // Initialize weight of MST Console.WriteLine('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (int i = edges.Count - 1; i >= 0; i--) { int u = edges[i].u; int v = edges[i].v; // Remove edge from undirected graph adj[u].Remove(v); adj[v].Remove(u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (IsConnected() == false) { adj[u].Add(v); adj[v].Add(u); // This edge is part of MST Console.WriteLine('({0} {1})' u v); mst_wt += edges[i].w; } } Console.WriteLine('Total weight of MST is {0}' mst_wt); } } class GFG { // Driver code static void Main(string[] args) { // create the graph given in above figure int V = 9; Graph g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.AddEdge(0 1 4); g.AddEdge(0 7 8); g.AddEdge(1 2 8); g.AddEdge(1 7 11); g.AddEdge(2 3 7); g.AddEdge(2 8 2); g.AddEdge(2 5 4); g.AddEdge(3 4 9); g.AddEdge(3 5 14); g.AddEdge(4 5 10); g.AddEdge(5 6 2); g.AddEdge(6 7 1); g.AddEdge(6 8 6); g.AddEdge(7 8 7); g.ReverseDeleteMST(); } } // This code is contributed by cavi4762
// Javascript program to find Minimum Spanning Tree // of a graph using Reverse Delete Algorithm // Graph class represents a directed graph // using adjacency list representation class Graph { // Constructor constructor(V) { this.V = V; this.adj = []; this.edges = []; for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) { this.adj[i] = []; } } // function to add an edge to graph addEdge(u v w) { this.adj[u].push(v);// Add w to v’s list. this.adj[v].push(u);// Add w to v’s list. this.edges.push([w [u v]]); } DFS(v visited) { // Mark the current node as visited and print it visited[v] = true; for (const i of this.adj[v]) { if (!visited[i]) { this.DFS(i visited); } } } // Returns true if given graph is connected else false isConnected() { const visited = []; for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++) { visited[i] = false; } // Find all reachable vertices from first vertex this.DFS(0 visited); // If set of reachable vertices includes all // return true. for (let i = 1; i < this.V; i++) { if (!visited[i]) { return false; } } return true; } // This function assumes that edge (u v) // exists in graph or not reverseDeleteMST() { // Sort edges in increasing order on basis of cost this.edges.sort((a b) => a[0] - b[0]); let mstWt = 0;// Initialize weight of MST console.log('Edges in MST'); // Iterate through all sorted edges in // decreasing order of weights for (let i = this.edges.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { const [u v] = this.edges[i][1]; // Remove edge from undirected graph this.adj[u] = this.adj[u].filter(x => x !== v); this.adj[v] = this.adj[v].filter(x => x !== u); // Adding the edge back if removing it // causes disconnection. In this case this // edge becomes part of MST. if (!this.isConnected()) { this.adj[u].push(v); this.adj[v].push(u); // This edge is part of MST console.log(`(${u} ${v})`); mstWt += this.edges[i][0]; } } console.log(`Total weight of MST is ${mstWt}`); } } // Driver code function main() { // create the graph given in above figure var V = 9; var g = new Graph(V); // making above shown graph g.addEdge(0 1 4); g.addEdge(0 7 8); g.addEdge(1 2 8); g.addEdge(1 7 11); g.addEdge(2 3 7); g.addEdge(2 8 2); g.addEdge(2 5 4); g.addEdge(3 4 9); g.addEdge(3 5 14); g.addEdge(4 5 10); g.addEdge(5 6 2); g.addEdge(6 7 1); g.addEdge(6 8 6); g.addEdge(7 8 7); g.reverseDeleteMST(); } main();
Излаз
Edges in MST (3 4) (0 7) (2 3) (2 5) (0 1) (5 6) (2 8) (6 7) Total weight of MST is 37
Временска сложеност: О((Е*(В+Е)) + Е лог Е) где је Е број ивица.
ц програм за поређење стрингова
Сложеност простора: О(В+Е) где је В број темена, а Е број ивица. Користимо листу суседности за складиштење графика тако да нам је потребан простор пропорционалан О(В+Е).
напомене:
- Горња имплементација је једноставна/наивна имплементација алгоритма Реверсе Делете и може се оптимизовати на О(Е лог В (лог лог В)3) [Извор: Недељу дана ]. Али ова оптимизована временска сложеност је и даље мања од Прим и Крускал Алгоритми за МСТ.
- Горња имплементација мења оригинални графикон. Можемо направити копију графикона ако се оригинални графикон мора задржати.
Креирај квиз
