С обзиром на корен а Бинарно стабло претраге и цео број к . Задатак је пронаћи највећи број у бинарном стаблу претраге тј мање од или једнаки на к ако такав елемент не постоји испиши -1.
Примери:
Улаз:
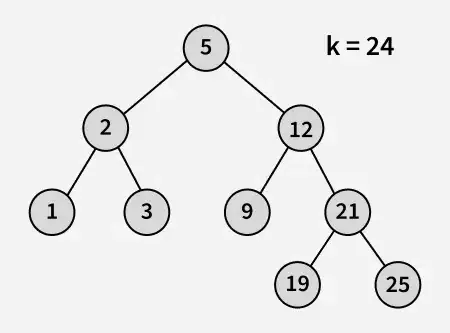
Излаз : 21
Објашњење: 19 и 25 су два најближа броја 21, а 19 је највећи број чија је вредност мања или једнака 21.
Улаз: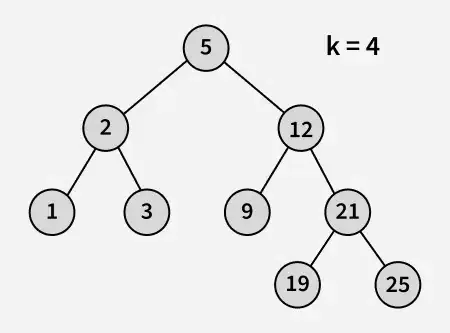
Излаз : 3
Објашњење: 3 и 5 су два најближа броја 4, а 3 је највећи број чија је вредност мања или једнака 4.
Садржај
- [Наивни приступ] Коришћење рекурзије - О(х) време и О(х) простор
- [Очекивани приступ] Коришћење итерације - О(х) време и О(1) простор
[Наивни приступ] Коришћење рекурзије - О(х) време и О(х) простор
C++Идеја је да почнемо од корен и упореди његову вредност са к. Ако је вредност чвора већа од к померите се на лево подстабло. У супротном пронађите вредност највећег броја мању од једнаког к у десно подстабло . Ако десно подстабло врати -1 (што значи да таква вредност не постоји) онда вратите вредност тренутног чвора. Else return the value returned by right subtree (as it will be greater than current node's value but less than equal to k).
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): # Base cases if root is None: return -1 if root.data == k: return k # If root's value is smaller # try in right subtree elif root.data < k: x = findMaxFork(root.right k) if x == -1: return root.data else: return x # If root's data is greater # return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k) if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { // Base cases if (root == null) return -1; if (root.data == k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { int x = FindMaxFork(root.right k); if (x == -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return FindMaxFork(root.left k); } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { // Base cases if (root === null) return -1; if (root.data === k) return k; // If root's value is smaller // try in right subtree else if (root.data < k) { let x = findMaxFork(root.right k); if (x === -1) return root.data; else return x; } // If root's data is greater // return value from left subtree. return findMaxFork(root.left k); } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Излаз
21
[Очекивани приступ] Коришћење итерације - О(х) време и О(1) простор
C++Идеја је да почнемо од корен и упореди његову вредност са к . Ако је вредност чвора <= k ажурирајте вредност резултата на роот вредност и пређите на право подстабло друго се помери на лево подстабло. Би итеративно Применом ове операције на свим чворовима можемо минимизирати простор потребан за рекурзија стек.
// C++ code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion #include
// Java code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { int data; Node left right; Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int findMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); System.out.println(findMaxFork(root k)); } }
# Python code to find the largest value # smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node: def __init__(self val): self.data = val self.left = None self.right = None # function to find max value less than k def findMaxFork(root k): result = -1 # Start from root and keep looking for larger while root is not None: # If root is smaller go to right side if root.data <= k: result = root.data root = root.right # If root is greater go to left side else: root = root.left return result if __name__ == '__main__': k = 24 # creating following BST # # 5 # / # 2 12 # / / # 1 3 9 21 # / # 19 25 root = Node(5) root.left = Node(2) root.left.left = Node(1) root.left.right = Node(3) root.right = Node(12) root.right.left = Node(9) root.right.right = Node(21) root.right.right.left = Node(19) root.right.right.right = Node(25) print(findMaxFork(root k))
// C# code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion using System; class Node { public int data; public Node left right; public Node(int val) { data = val; left = null; right = null; } } class GfG { // function to find max value less than k static int FindMaxFork(Node root int k) { int result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root != null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } static void Main() { int k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 Node root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); Console.WriteLine(FindMaxFork(root k)); } }
// JavaScript code to find the largest value // smaller than or equal to k using recursion class Node { constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.left = null; this.right = null; } } // function to find max value less than k function findMaxFork(root k) { let result = -1; // Start from root and keep looking for larger while (root !== null) { // If root is smaller go to right side if (root.data <= k) { result = root.data; root = root.right; } // If root is greater go to left side else { root = root.left; } } return result; } let k = 24; // creating following BST // // 5 // / // 2 12 // / / // 1 3 9 21 // / // 19 25 let root = new Node(5); root.left = new Node(2); root.left.left = new Node(1); root.left.right = new Node(3); root.right = new Node(12); root.right.left = new Node(9); root.right.right = new Node(21); root.right.right.left = new Node(19); root.right.right.right = new Node(25); console.log(findMaxFork(root k));
Излаз
21Креирај квиз


